8. Performance Report
RbFly library is implemented with performance in mind. For example
RbFly can be over 4 times faster than other, similar solutions when publishing messages to a streaming broker (see Section 8.1.1)
RbFly’s AMQP 1.0 codec can be over 23 times faster compared to other AMQP 1.0 codecs (see Section 8.3.1)
Performance of RbFly is achieved by implementing critical sections of code using Cython, avoiding copying of data, and testing. The testing involves use of asyncio drop-in replacement uvloop, which improves performance of Python asyncio based applications.
Next sections of the report describe the results of the performance tests executed during RbFly project development
throughput of publishing messages to a streaming broker
throughput of publishing messages in AMQP 1.0 format to a RabbitMQ stream
throughput of encoding and decoding messages using AMQP 1.0 codec
Note
Results of performance testing might be affected by bias of a test scenario, or local conditions. Please submit a ticket in RbFly project’s issues system to propose an improvement to the performance testing procedures, the scripts, and the documentation of the project.
8.1. Publishing Messages
The test measures the performance of sending messages to a streaming broker. There are two subtests
publish single message, and receive confirmation from a broker for the message
publish batch of 100 messages, and receive confirmation from a broker for the batch
Section 8.1.2 outlines the testing procedure.
RbFly performance is tested against Python asyncio libraries for streaming technologies like RabbitMQ Streams, or Apache Kafka, see Section 8.4.1 for additional details.
8.1.1. Results
The combination of RbFly library and RabbitMQ Streams broker can publish messages two times faster (single message) or over 4 times faster (batch of 100 messages) comparing to similar solutions for Python language.
The summary of message publishing performance test is presented on Figure 8.1.
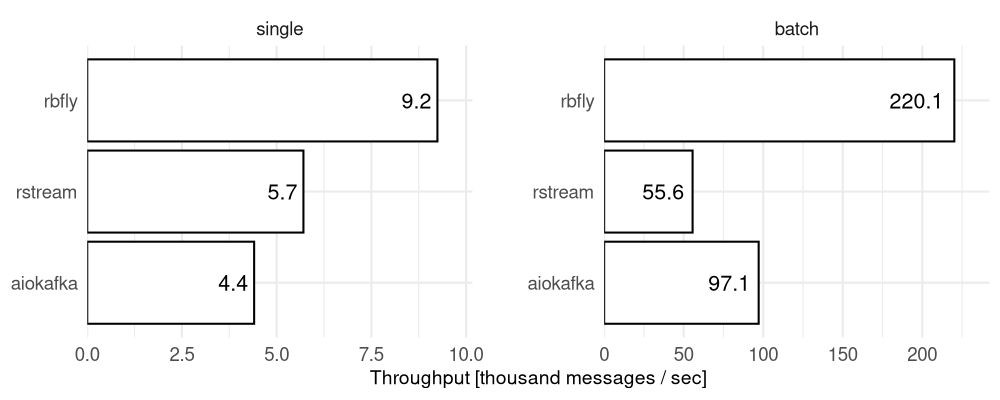
Figure 8.1 Performance of message publishing by RbFly, and related libraries
Median number of published messages per second for RbFly, rstream, and aiokafka libraries. The libraries send single message (left panel) or batch of 100 messages (right panel).
8.1.2. Test Scenario
The performance testing scenario is as follows
Publish 200 thousand messages to a broker. Receive a confirmation from the broker for each message - single message publishing test.
Publish 1 million messages, in batches of 100 messages, to a broker. Receive a confirmation from the broker for each batch.
Each message is 10 bytes.
RabbitMQ Streams client libraries publish messages in AMQP format.
Apache Kafka client libraries publish messages using MessagePack binary format.
Repeat each round of testing 100 times.
Calculate median value of number of messages published to a broker, and present as a bar plot.
8.2. Publishing Messages in AMQP Format
The test measures the performance of publishing messages using RbFly project’s AMQP encoder. This is compared against sending simple binary string messages. There are two subtests
publish single message, and receive confirmation from a broker for the message
publish batch of 100 messages, and receive confirmation from a broker for the batch
8.2.1. Results
RbFly’s AMQP encoder affects throughput of publishing messages to RabbitMQ Streams broker. However, the observed difference is small when sending messages in AMQP format compared to sending messages as a binary string.
The summary of the performace test of publishing messages in AMQP format is presented on Figure 8.2.
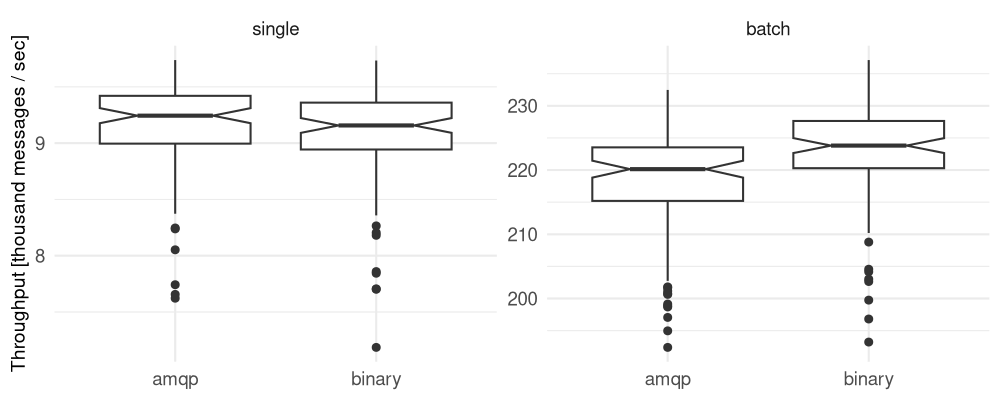
Figure 8.2 Throughput of publishing messages in AMQP format and as a binary string
Median number of published messages per second using RbFly’s AMQP encoder and as a binary string. RbFly sends single message (left panel) or batch of 100 messages (right panel).
8.2.2. Test Scenario
The scenario for performance testing of publishing messages in AMQP format is as follows
Publish 200 thousand messages to a broker. Receive a confirmation from the broker for each message - single message publishing test.
Publish 1 million messages, in batches of 100 messages, to a broker. Receive a confirmation from the broker for each batch.
Repeat each scenario by publishing message in AMQP format, or using a binary string.
Each message is a string of length 10 before encoding as AMQP, or as a binary string.
Repeat each round of testing 100 times.
Calculate median value of number of messages published to a broker, and present as a box plot.
A binary string for a test is generated using consecutive numer of a message, for example in Python language:
'{:010d}'.format(1357).encode()
which encodes the binary string:
b'0000001357'
8.3. Encoding and Decoding with AMQP Codec
The test measures performance of encoding and decoding data with AMQP 1.0 codecs implemented by RbFly, rstream, and Qpid Proton libraries (see also Section 8.4.1).
Section 8.3.2 outlines the testing procedure.
8.3.1. Results
RbFly’s AMQP 1.0 codec is order of magnitude faster than codecs implemented by rstream and Qpid Proton projects.
The summary of the performace test of AMQP 1.0 codecs is presented on Figure 8.3.
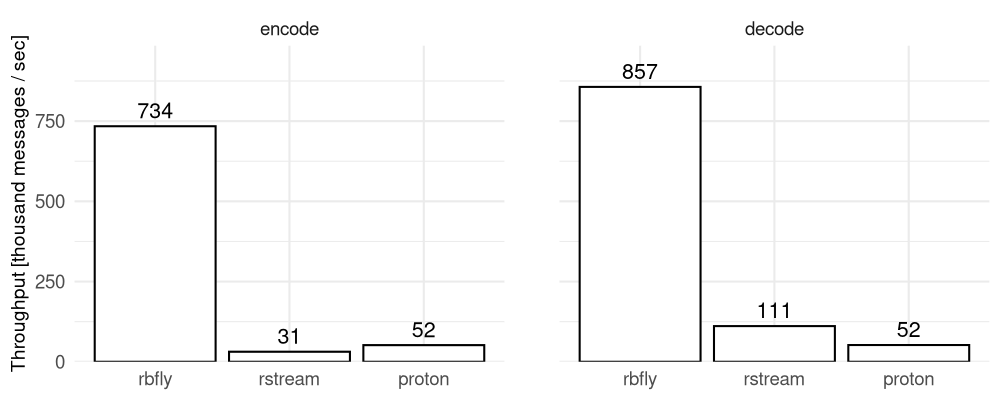
Figure 8.3 Performance of encoding and decoding of message data with AMQP codecs
Number of encoded (left panel) and decoded (right panel) messages per second by AMQP 1.0 codecs implemented by RbFly, rstream, and Qpid Proton projects.
8.3.2. Test Scenario
The performance test of AMQP 1.0 codecs processes data of a single AMQP 1.0
message. A message is encoded and decoded 10 thousand times. The execution
time is measured with Python’s timeit.timeit() function, and
normalized to a number of processed messages per second.
The data of a AMQP 1.0 message is a dictionary, which consists of strings, binary strings, and integers:
{
'large-int': 2 ** 31 - 1,
'small-list': [1, 2, 3],
'bin-string': b'abc',
}
8.4. Testing Environment
8.4.1. Software Components
The following software components are used during RbFly project performance testing
- aiokafka 0.12.0
aiokafka is a client library for Apache Kafka distributed event streaming platform.
- Apache Kafka 4.1.0
Apache Kafka is a distributed event streaming platform.
The broker is using Apache Kafka Raft as quorum controller.
Its configuration option
log.dirsis set to/var/tmp/kafka-logs- the directory points to permanent storage.
- Qpid Proton 0.40.0
Qpid Proton is a messaging library, which integrates with AMQP 1.0 ecosystem from any platform.
- RabbitMQ 4.2.0
RabbitMQ Streams is a streaming solution, which is part of RabbitMQ message broker project.
- rstream 0.40.0
rstream is a Python client library for RabbitMQ Streams.
rstream provides AMQP codec copied from Azure Event Hubs project by Microsoft.
8.4.2. Hardware Configuration
The performance tests are executed on a laptop with the following configuration
Intel CPU i5-1135G7, 2.40GHz
32 GB RAM
Samsung SSD 990 PRO 4TB
When running the performance tests
the Intel’s Turbo Boost Technology is switched off
Linux CPU scaling governor is set to performance